Understanding Surface Finishing: Definition, Techniques, and Importance
- Release Date: April 26, 2024
Understanding Surface Finishing: Definition, Techniques, and Importance
Introduction
In the world of manufacturing, surface finishing holds immense significance. Understanding its intricacies is crucial for enhancing product quality and meeting industry standards. NowFab, a leading digital manufacturing platform, delves into the realm of surface finishing to elucidate its importance in modern manufacturing processes.
Definition of Surface Finishing
Surface finishing is a critical process in manufacturing that involves refining a part’s surface to achieve desired properties such as aesthetics, functionality, and durability. This technique encompasses a variety of methods, including polishing, buffing, and coating, each tailored to specific material types and project requirements. Surface finishing not only enhances the appearance of a product but also improves its performance by reducing friction, increasing wear resistance, and providing protection against environmental factors. Understanding the definition of surface finishing is essential for engineers and designers aiming to optimize their product’s quality and market competitiveness.
Common Surface Finishing Techniques
The diverse array of surface finishing techniques employed in manufacturing:
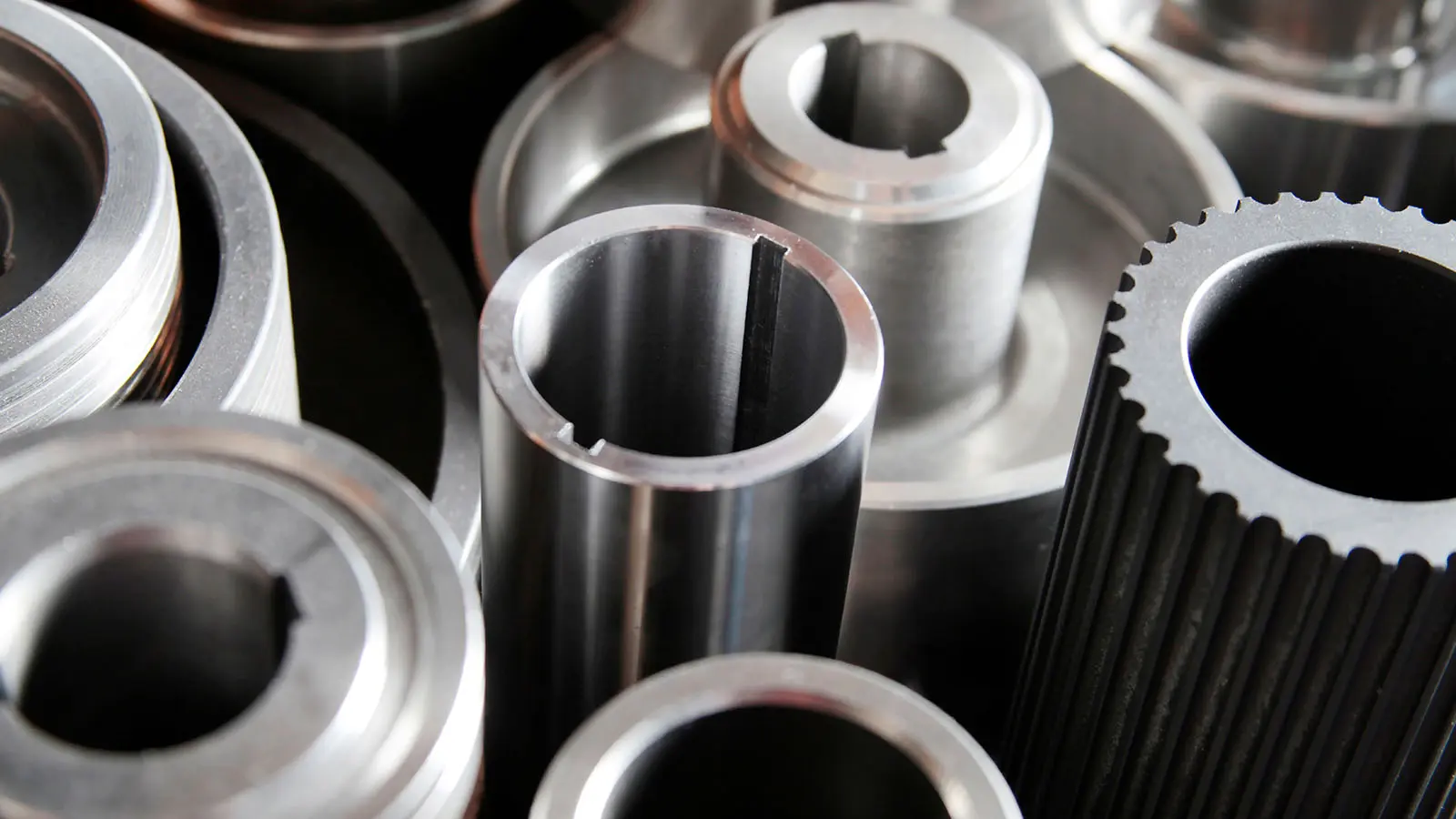
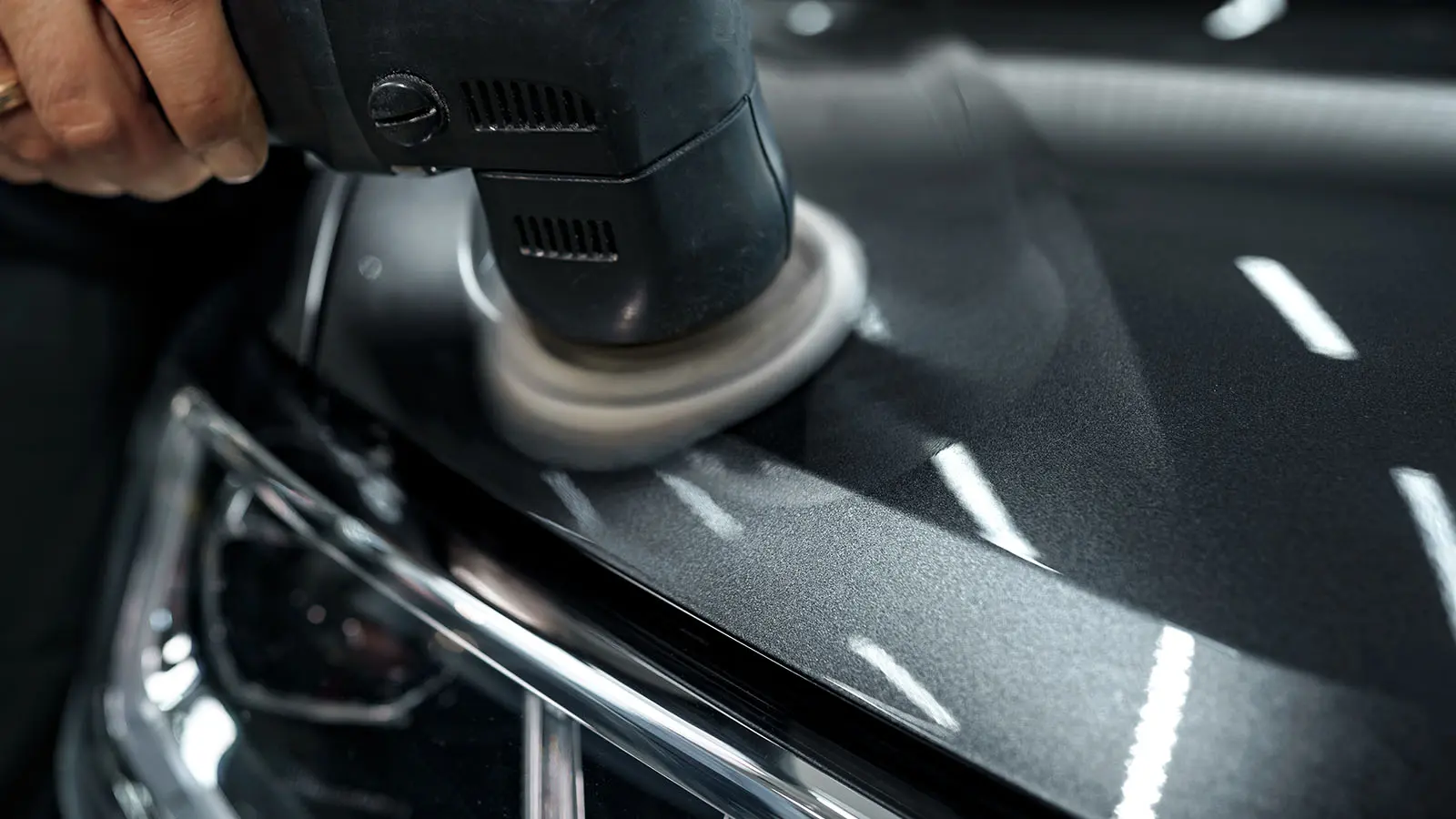
- Mechanical Finishing Techniques are integral to achieving the desired surface textures and smoothness on various materials. A real-world example of this process is the preparation of a wooden surface for a fine piece of furniture. Sanding is initially used to remove roughness and imperfections, followed by progressively finer grades of sandpaper to achieve a mirror-like finish. In the automotive industry, grinding and polishing are employed to smooth out metal components after casting or forging, ensuring a flawless finish before painting or further assembly.
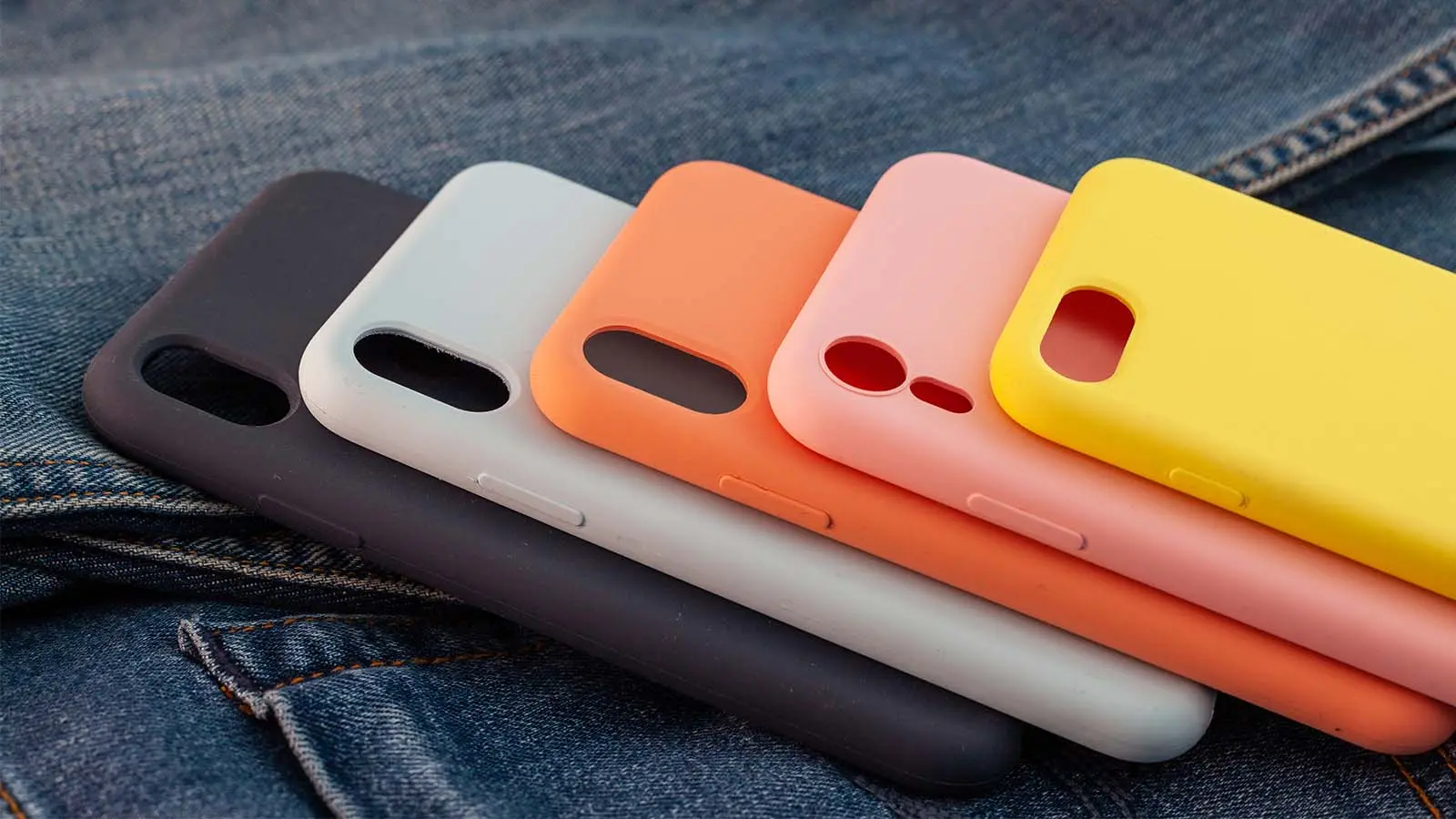
- Chemical Finishing Techniques are particularly useful for altering the surface properties of materials through chemical reactions. A common example is the anodizing process used on aluminum surfaces. Anodizing not only provides a decorative effect but also increases the material’s resistance to wear and corrosion. For instance, in the production of mobile phone cases, aluminum is often anodized to achieve a durable, colored finish that can withstand daily wear and tear.
- Electroplating and Electrochemical Techniques are widely used to deposit thin layers of metals onto surfaces, enhancing their appearance and functional properties. A practical example is the application of a gold plating layer on electrical contacts to improve conductivity and longevity. Similarly, chrome plating on automotive components is a standard practice to provide a shiny, rust-resistant surface that maintains the vehicle’s aesthetic appeal.
- Thermal Finishing Techniques modify the surface properties of materials through controlled heating and cooling processes. An example of this is the heat treatment of steel, where components are heated to a specific temperature and then cooled to alter their hardness and strength. This process is crucial in the manufacturing of tools and machinery, where high wear resistance and durability are required. Flame spraying, another thermal technique, is used to apply a coating of a more resistant material onto a metal surface, such as when applying a layer of stainless steel onto a carbon steel pipe to enhance its corrosion resistance.
Importance of Surface Finishing
Surface finishing offers manifold benefits crucial for manufacturing success:
- Enhancing Aesthetics and AppearanceSurface finishing techniques play a crucial role in enhancing the visual appeal of products, which significantly contributes to brand perception and consumer satisfaction. A real-world example is the use of polishing in the automotive industry. Car manufacturers employ various polishing methods to achieve a glossy, reflective finish on car exteriors, making the vehicles more attractive to potential buyers. This attention to aesthetics not only boosts the car’s resale value but also creates a positive brand image associated with quality and luxury.
- Improving Functionality and PerformanceSurface treatments, such as coating and plating, are essential for improving product functionality by enhancing wear resistance, reducing friction, and optimizing surface properties for specific applications. For instance, in the electronics industry, a thin layer of gold is often electroplated onto connectors to ensure excellent electrical conductivity and minimize resistance. This plating process not only improves the performance of electronic devices but also protects the connectors from corrosion, prolonging the device’s lifespan.
- Providing Protection Against Corrosion, Wear, and Environmental FactorsSurface finishing techniques like anodizing and coating offer protective layers that shield products from corrosion, abrasion, and environmental damage, ensuring longevity and reliability. A practical example is the use of anodizing on aluminum products, such as laptop cases and smartphone frames. Anodizing creates a hard, wear-resistant surface that is also resistant to corrosion, providing a durable and protective finish that can withstand daily use. This protective layer not only enhances the product’s lifespan but also maintains its appearance over time, offering consumers value and peace of mind.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding surface finishing is paramount in modern manufacturing. NowFab emphasizes the significance of mastering surface finishing techniques to achieve superior product quality, performance, and aesthetics. By harnessing the knowledge and expertise offered by NowFab, manufacturers can elevate their products to new heights of excellence and competitiveness in today’s dynamic market landscape.
Try NOWfab Now!
All information and uploads are secure and confidential.
Latest Blog Posts
Stay at the forefront of industry innovation by reading our latest blog post.