Top 5 Sheet Metal Materials: A Guide to Choosing the Right for Your Project
- Release Date: April 28, 2024
Top 5 Sheet Metal Materials: A Guide to Choosing the Right for Your Project
Introduction to Sheet Metal Materials
Material selection plays a pivotal role in sheet metal processing, significantly influencing the final product’s quality, performance, and cost. The choice of material is not merely a matter of preference but a strategic decision that can determine the success of a project. High-quality materials ensure durability and reliability, while the right grade can optimize performance under specific conditions. For instance, selecting a material with high tensile strength is crucial for parts that endure heavy loads. Additionally, material properties such as thermal conductivity, electrical resistance, and corrosion resistance must align with the product’s intended use. Cost-effectiveness is another critical factor; premium materials may offer superior qualities but can escalate costs. Balancing material properties with budget constraints is essential for profitability. In summary, thoughtful material selection is the cornerstone of successful sheet metal processing, ensuring that the end product meets the desired standards without compromising on cost efficiency.
The 5-sheet Metal Materials
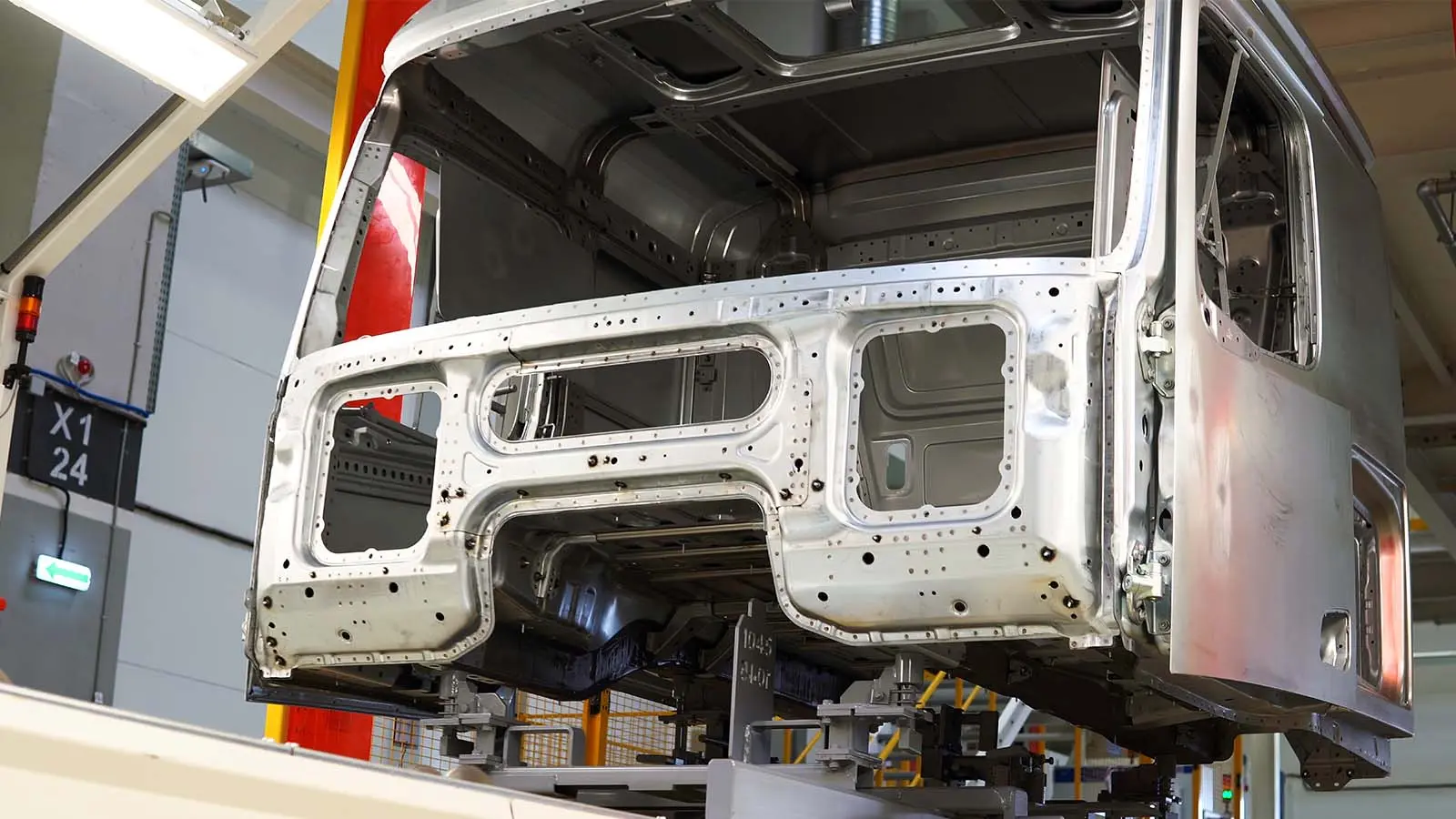
1. Cold Rolled Sheet (SPCC)
Cold-rolled steel (SPCC) is renowned for its exceptional surface quality and precise dimensional accuracy, making it a preferred material for precision applications. This steel variety undergoes a cold rolling process, which refines its grains and eliminates surface imperfections, resulting in a smooth, uniform texture. Its high dimensional consistency ensures that manufactured parts meet stringent specifications, ideal for industries like automotive, where tolerances are critical. The superior surface finish of SPCC steel allows for a wide range of secondary operations, from painting to plating, without the need for extensive pre-treatment. This not only enhances the aesthetic appeal but also improves the product’s durability and resistance to environmental factors. Given these attributes, cold-rolled steel is a popular choice for components that demand a high-quality finish and exacting standards, such as automotive panels, precision instruments, and architectural applications.
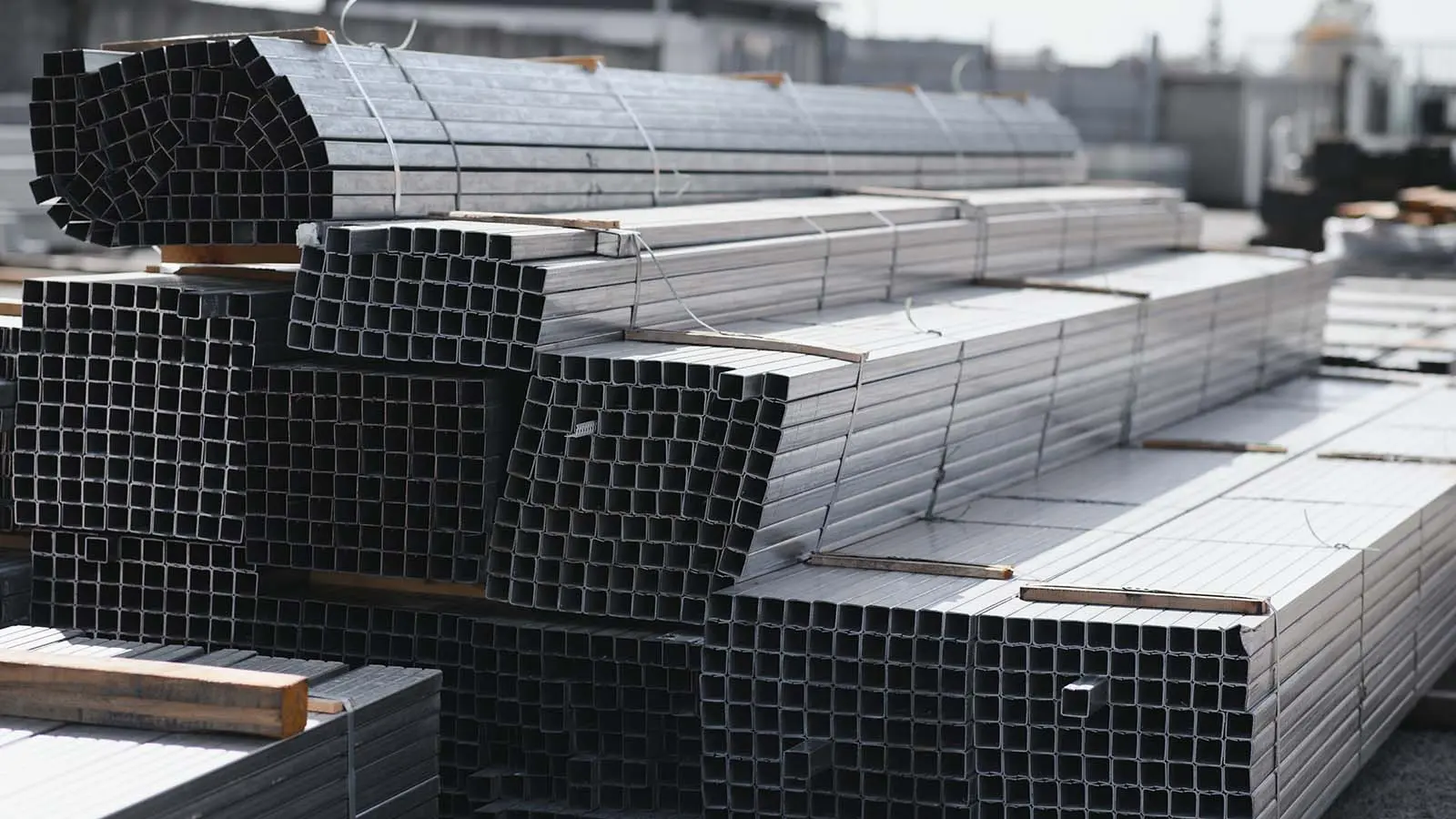
2. Hot Rolled Sheet (SHCC)
Hot-rolled steel (SHCC) is distinguished by its manufacturing process, which involves rolling steel at high temperatures, resulting in a rougher surface and greater tolerances compared to cold-rolled steel. This method imparts a unique set of properties, including enhanced ductility and workability, making it suitable for applications where material must withstand heavy loads or be shaped into complex forms. The cost-effectiveness of hot-rolled steel, due to its simpler production process, also makes it an attractive option for large-scale projects. It’s commonly used in construction for beams, bridges, and automotive frames, where structural integrity is paramount. Despite its less refined surface, hot rolled steel’s robustness and adaptability make it the material of choice for functional applications where strength and economy are key considerations.
3. Galvanized Sheets (SECC, SGCC)
Galvanized steel, available in SECC (electro-galvanized) and SGCC (hot-dipped galvanized) forms, is a versatile material known for its corrosion resistance and suitability for electroplating. The electroplating process enhances its surface properties, making it ideal for applications requiring a combination of strength and a refined appearance. SECC steel, with its thinner coating, is favored for components that need a smooth, paintable surface, such as automotive exteriors and electronic chassis. SGCC, with its thicker zinc coating, is often chosen for construction materials and outdoor applications where durability and protection from the elements are crucial. Both types offer a wide range of applications, from automotive parts to construction materials, showcasing galvanized steel’s adaptability and reliability in various industries.
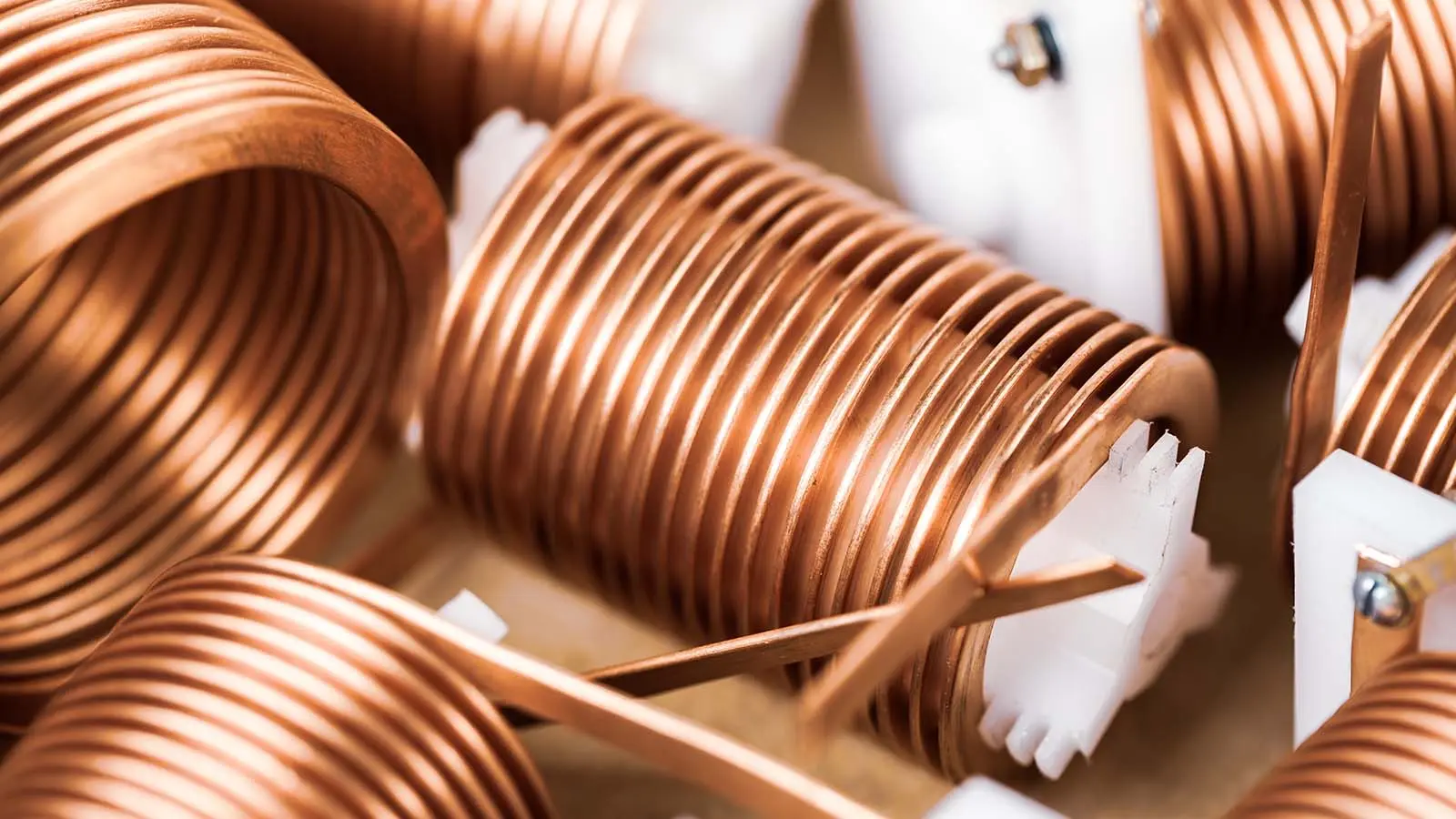
4. Copper and Copper Alloys
Copper materials are celebrated for their exceptional strength and durability, making them ideal for a myriad of sheet metal fabrication applications. Known for its excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, copper also boasts high malleability and ductility, allowing for intricate designs and shapes. Varieties such as brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, offer increased wear resistance and antimicrobial properties, perfect for decorative and sanitary applications. Bronze, a copper-tin alloy, enhances strength and corrosion resistance, often used in marine and high-stress environments. Beryllium copper stands out for its non-magnetic properties and high electrical conductivity, favored in electrical contacts and springs. Each type of copper brings unique attributes to the table, catering to specific industrial needs and preferences.
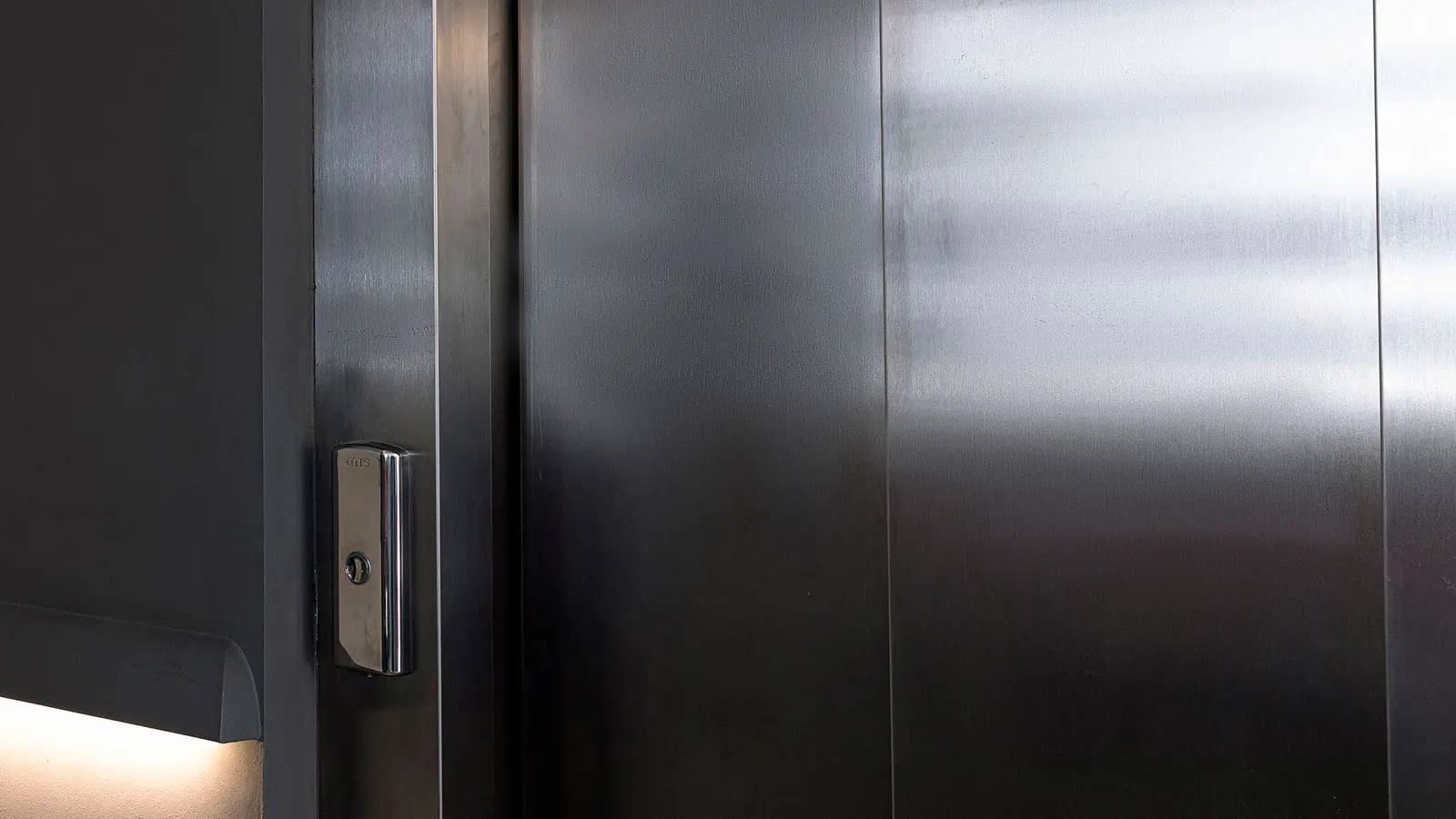
5. Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is renowned for its superior corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, attributes that have solidified its popularity in both functional and decorative applications. Its lustrous finish and robustness make it a top choice for environments exposed to moisture and chemicals. The variety of surface finishes enhances its versatility; mirror finishes provide a reflective, pristine look, ideal for modern architecture and upscale interiors. Hairline finishes offer a subtle, smooth texture, often used in appliances and elevators for a sleek appearance. Satin finishes, with their soft, non-reflective sheen, are favored for their understated elegance in both commercial and residential settings. Each finish caters to specific design requirements, ensuring stainless steel remains a versatile and stylish material option.
Real-world Applications
Cold-rolled steel, known for its precision and high surface quality, is exemplified in automotive panel manufacturing, which reveals its benefits, including dimensional accuracy that ensures panels fit perfectly, and its formability that facilitates complex design implementations. This leads to enhanced vehicle safety and streamlined aesthetics, with reduced production costs due to its high manufacturing efficiency.
In modern architecture, stainless steel’s adaptability and visual allure are highlighted through cladding applications, which demonstrates how its corrosion resistance and low maintenance requirements make it an ideal material for exterior facades, especially in coastal regions. The material’s reflective properties and diverse finish options allow architects to create visually striking and sustainable structures that stand the test of time.
Conclusion
In summary, material selection in sheet metal processing is paramount, impacting product quality, performance, and cost. Cold-rolled steel (SPCC) is favored for precision applications due to its high surface quality and dimensional accuracy. Hot rolled steel (SHCC) offers ductility and cost-effectiveness, ideal for structural components. Galvanized steel, including SECC and SGCC, provides corrosion resistance and is suitable for electroplating, with a wide range of applications from automotive to construction. Copper materials, such as brass and bronze, are chosen for their strength and durability, while beryllium copper is valued for its conductivity and non-magnetic properties. Stainless steel stands out for its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, with various finishes for different applications, from automotive panels to architectural cladding. Each material brings unique advantages, tailoring to specific industrial needs.
Try NOWfab Now!
All information and uploads are secure and confidential.
Latest Blog Posts
Stay at the forefront of industry innovation by reading our latest blog post.