Mastering Digital Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Printing Techniques
- Release Date: April 25, 2024
Overview of 3D Printing Technology
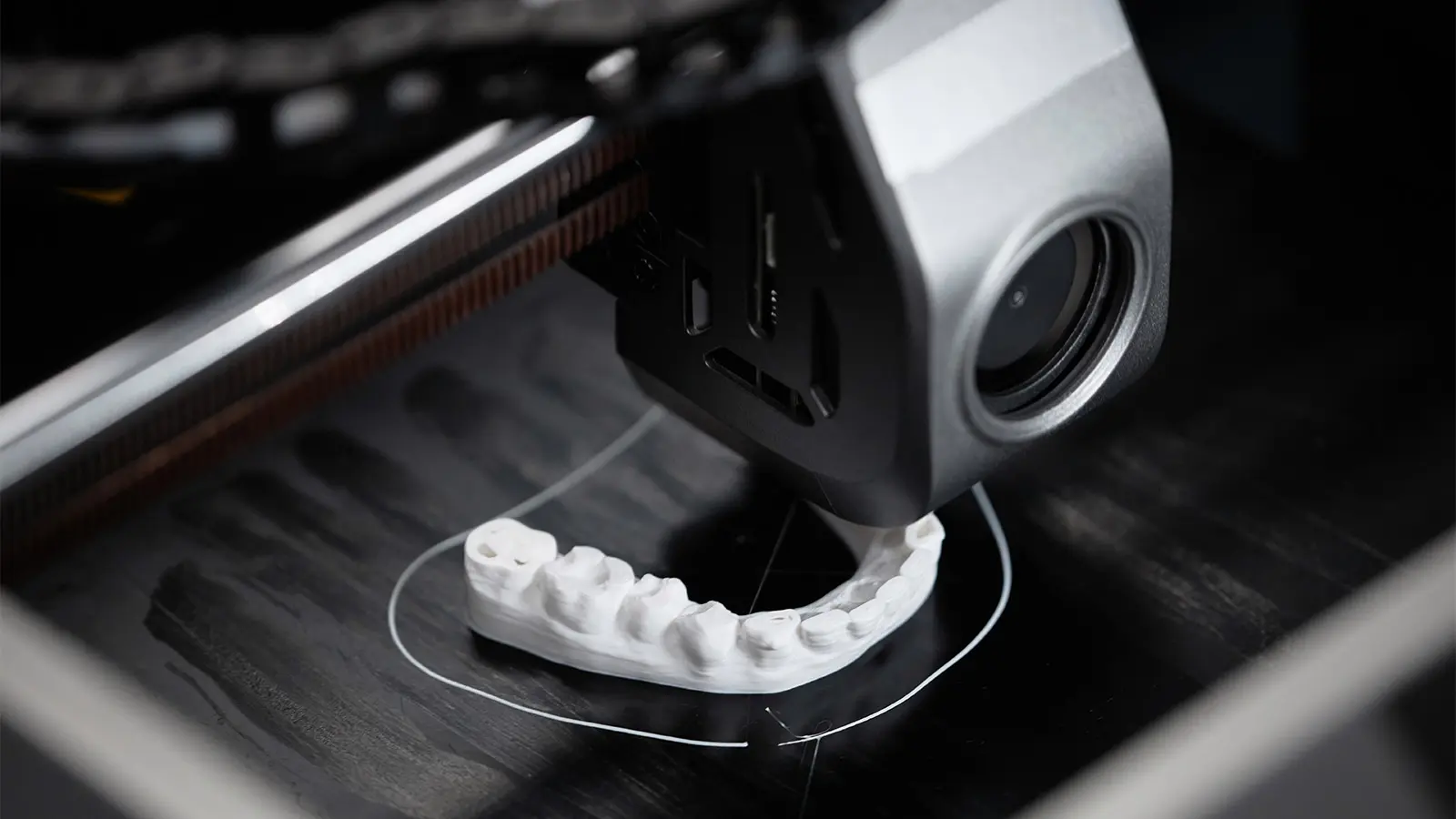
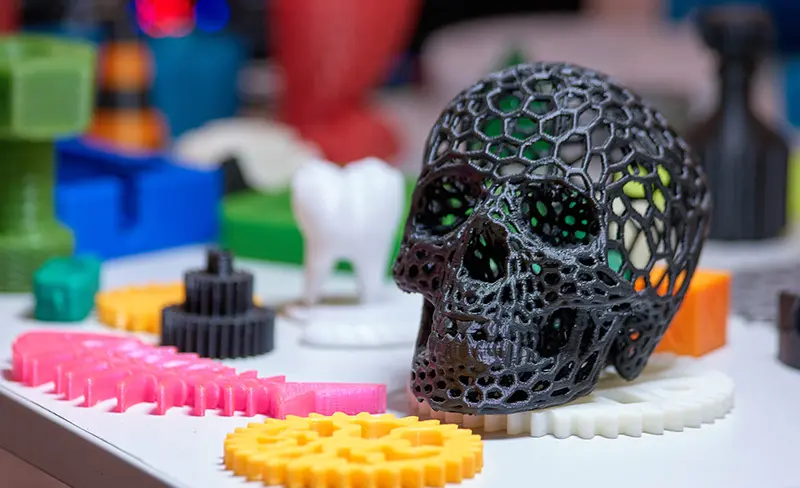
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a cutting-edge technology that revolutionizes the way we create physical objects. At the core of this process is the ability to layer materials—such as polymers, metals, and composites—to build complex structures from digital models.
The techniques used in 3D printing vary and include Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). FDM is widely accessible and uses thermoplastics, making it ideal for prototyping and low-volume production. SLA, on the other hand, employs ultraviolet light to cure liquid resins into solid objects, resulting in high-resolution prints suitable for intricate designs. SLS is known for its use of powder-based materials and is particularly effective for producing complex geometries and functional parts with multiple components in a single build.
3D printing has broad applications across industries. In healthcare, it accelerates the development of prosthetics and personalized medical devices. The aerospace industry benefits from its ability to create lightweight and durable components, enhancing fuel efficiency and performance. In automotive manufacturing, 3D printing streamlines the production of custom parts and contributes to rapid prototyping.
NOWfab.com, as a digital manufacturing platform, offers these 3D printing services, enabling customers to bring their designs to life with precision and efficiency. From rapid prototyping to end-use part production, NOWfab.com’s 3D printing solutions are designed to meet the diverse needs of innovators and manufacturers alike.
Materials of 3D Printing
Polymeric Materials in 3D Printing
Polymeric materials are the workhorses of the 3D printing industry, offering a balance of affordability, ease of use, and versatility. The most common polymer used is PLA (Polylactic Acid), derived from renewable resources, it is biodegradable and favored for its ease of printing and low odor. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is another popular choice, known for its high-impact resistance and temperature tolerance, making it suitable for functional parts. Furthermore, PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol) stands out for its strength, thermal stability, and resistance to chemicals, often chosen for outdoor applications and food-contact items. These polymeric materials empower designers and engineers to rapidly prototype and manufacture a wide array of products, from household items to complex mechanical parts.
Metal Materials in 3D Printing
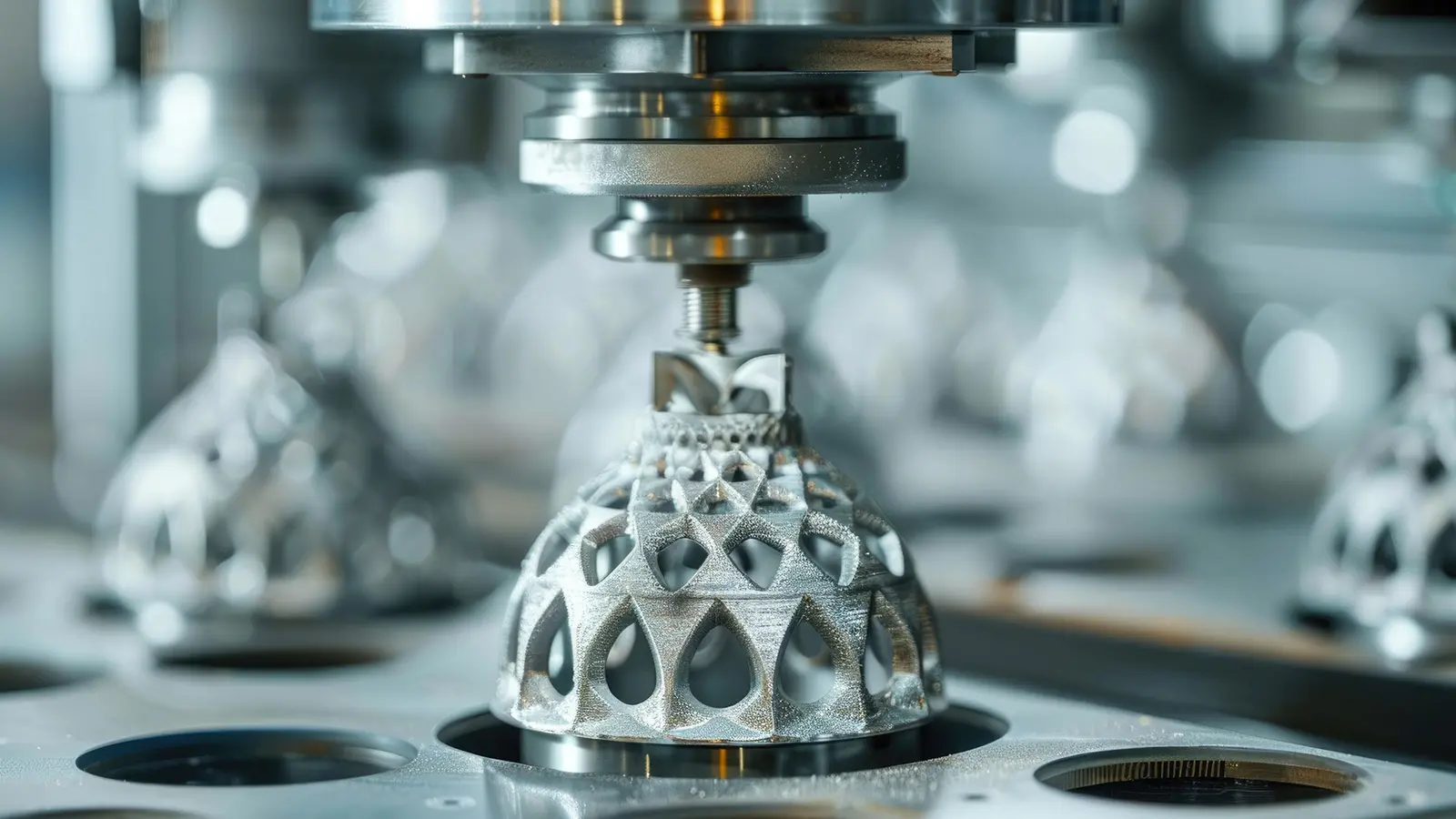
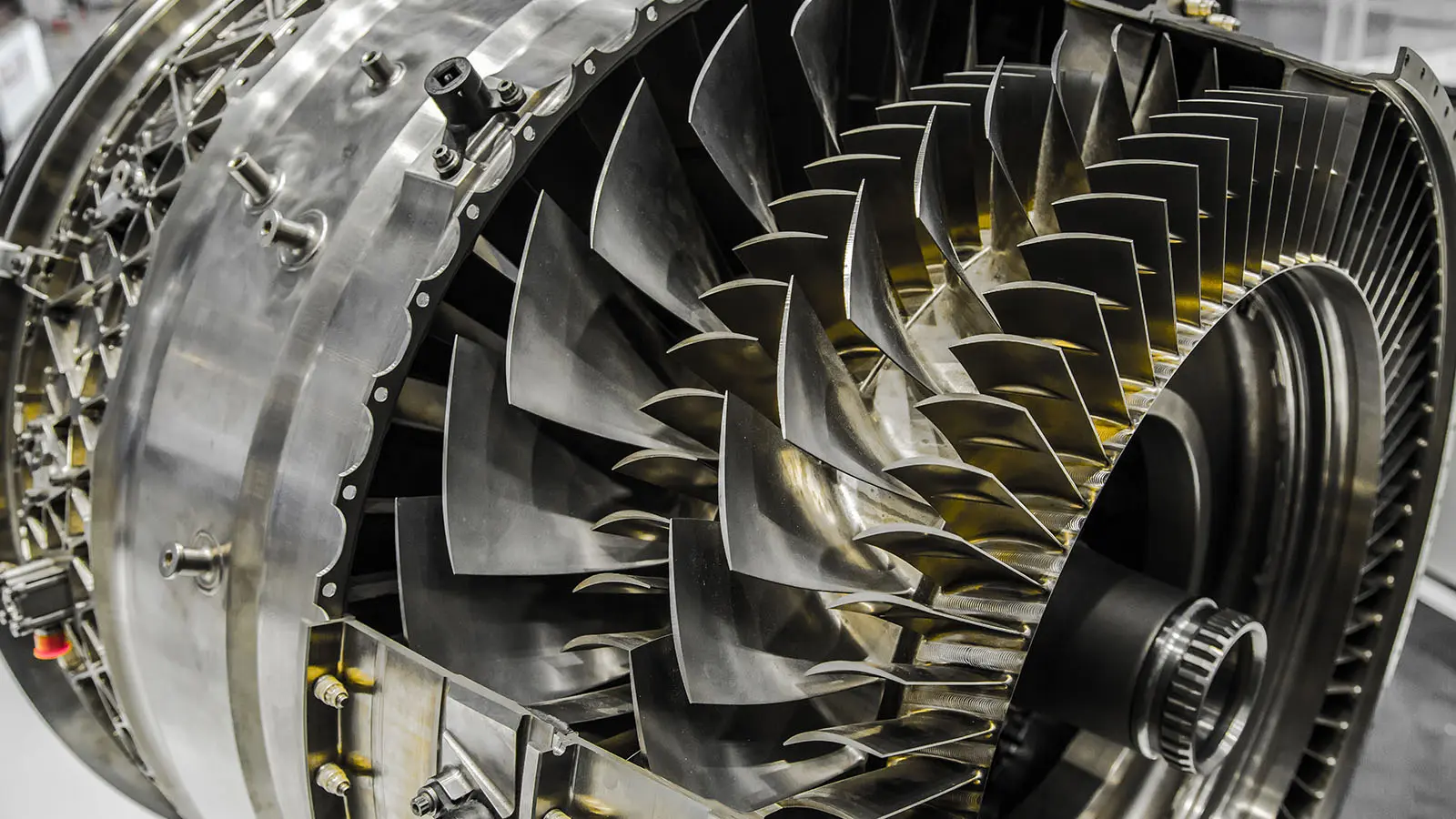
Metal 3D printing has gained significant traction for its ability to produce high-strength, complex, and durable components. Materials like stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium alloys are used to create parts that require mechanical integrity and resistance to extreme conditions. For instance, Inconel, a family of austenitic nickel-chromium-based superalloys, is chosen for its excellent corrosion and heat resistance, crucial for aerospace applications. Similarly, tool steel is favored for manufacturing cutting tools and dies due to its high wear resistance. Metal 3D printing processes, such as Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF) and Electron Beam Melting (EBM), allow for the creation of intricate geometries and lattice structures that were previously unattainable, leading to weight reduction and performance enhancement in final products. NOWfab.com leverages these advanced materials and techniques to cater to industries where the performance and longevity of components are paramount.
Application Domains of 3D Printing
3D Printing in Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, 3D printing is a game-changer, streamlining the production process by enabling rapid prototyping and reducing the time from design to market. This technology allows for the creation of complex geometries that traditional manufacturing methods might find prohibitive. Customized parts can be produced on-demand, which is particularly beneficial for small-batch production and personalized items. Furthermore, 3D printing minimizes material waste, aligning with modern sustainability goals.
3D Printing in Healthcare
The healthcare industry has experienced a significant impact from 3D printing, particularly in the areas of medical device development and patient-specific prosthetics. Customizable and precise, 3D printed prosthetics and orthotics offer a high degree of personalization, enhancing patient comfort and functionality. Moreover, this technology facilitates the creation of anatomical models for surgical planning, leading to better patient outcomes through more accurate and rehearsed surgeries.
3D Printing in Aviation
In aviation, 3D printing is used to produce lightweight components, which is critical for improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. The technology supports the manufacturing of complex parts with integrated functionalities, thereby reducing the need for assembly and maintenance. Additionally, 3D printed parts can be rapidly produced, which is advantageous for quick replacement of worn or damaged components, thereby minimizing downtime and enhancing operational efficiency. NOWfab.com’s digital manufacturing platform harnesses these capabilities to cater to the specific needs of the aviation industry.
Technological Advances and Future Prospects
Technological advances in 3D printing are propelling the industry forward with innovations that enhance precision, speed, and material diversity. Developments in software are improving design capabilities, while hardware enhancements are increasing build sizes and resolutions. The future of 3D printing holds promise for widespread adoption in various sectors, including significant strides in sustainable practices with the development of more eco-friendly materials. The prospect of 3D printed housing and infrastructure also signals a transformative impact on construction. As research continues, the technology is expected to become more accessible, potentially revolutionizing supply chains and personal fabrication, leading to a more decentralized and customized manufacturing landscape.
Try NOWfab Now!
All information and uploads are secure and confidential.
Latest Blog Posts
Stay at the forefront of industry innovation by reading our latest blog post.